Statement from the European Specialist Dietetic Network (ESDN) on Diabetes for World Diabetes Day 2024
This year’s World Diabetes Day focuses on “Diabetes and well-being” highlighting the role of dietitians, in managing diabetes effectively and improving overall well-being. Dietitians play a key role in helping individuals living with diabetes, normalize their blood glucose levels but also live healthier and more fulfilling lives.
Dietitians are trained healthcare professionals who combine nutrition knowledge with mental and physical health strategies to assist individuals achieve balance and resilience throughout their diabetes journey. By aiming at the adoption of long-lasting behaviours, dietitians provide personalized dietary advice, practical assistance, and empathy to individuals which can eventually contribute to the improvement of both physical and emotional well-being. ESDN Diabetes advocates for recognizing well-being as an essential aspect of quality diabetes care for those at risk or already diagnosed with diabetes is a focus for dietitians. Advancements, in technology like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and mobile apps, have revolutionized diabetes management by helping individuals analyze their blood glucose levels effectively and make informed decisions, about their diet while staying engaged in their healthcare journey.
In light of World Diabetes Day, we reaffirm our commitment to improving diabetes care through personalized, innovative, and holistic approaches. We aim for continued investment in dietetic services and technology integration to promote diabetes self-management and enhance overall well-being.
Diabulimia Infographic: Let’s Talk About Diabulimia
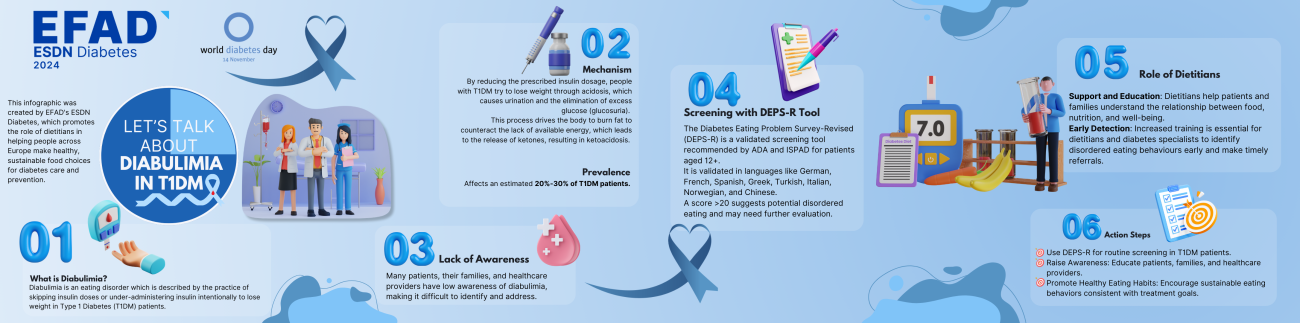
For World Diabetes Day, ESDN Diabetes has also launched an infographic focused on Diabulimia in Type 1 Diabetes (T1DM) to help dietitians address this critical yet under-recognized issue.
Diabulimia, an eating disorder where individuals with T1DM intentionally skip or reduce insulin doses to lose weight, carries serious health risks, including ketoacidosis. Affecting an estimated 20-30% of individuals with T1DM, diabulimia often goes undetected. Our infographic provides essential information to help dietitians detect and address diabulimia, with insights into warning signs, screening tools, and guidance on early intervention.
The infographic is available in a downloadable PDF. Join us in spreading awareness of Diabulimia and supporting the well-being of individuals with T1DM.
Webinar: Fat and Protein Counting in Type 1 Diabetes
Date & Time: Tuesday, November 19, 2024, at 18:00 CET
Register: here
In addition to the infographic, ESDN Diabetes is hosting a webinar on “Fat and Protein Counting in Type 1 Diabetes.” This webinar will cover the importance of fat and protein counting in type 1 diabetes management, especially where traditional carbohydrate counting may not be sufficient, such as for meals high in fat and protein.
ISA Video Collaboration for #WDD2024
The International Sweeteners Association (ISA) has collaborated with EFAD’s ESDN Diabetes to create a video for World Diabetes Day 2024. This video highlights the role of nutrition and dietitians in improving well-being and quality of life for people with diabetes.
Featured experts from EFAD’s ESDN Diabetes include:
- Maria Vasiloglou, PhD – Specialist in Nutrition and Digital Health at Nestlé Institute of Health Sciences, Switzerland, and ESDN Diabetes Committee Lead
- Joanna Ostrowska, PhD – Assistant Professor at the Medical University of Warsaw, Poland
- Martina Karbanová – Methodology Lead in Vitadio, Czech Republic
Together with ISA’s Nutrition Science Director, Vicky Pyrogianni, the experts discuss how nutrition and dietary guidance play a central role in diabetes care, well-being, and quality of life. Watch the video to learn more about the impact of dietitians on diabetes management.
References for the Infographic
- Apergi Κ., Romanidou Μ., Abdelkhalek H., Tripsianis G., Gonidakis F. Reliability and validity of the Diabetes Eating Problem Survey in Greek adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Psychiatrike. 2020;31:310–320. doi: 10.22365/jpsych.2020.314.310.
- Atik Altınok Y., Özgür S., Meseri R., Özen S., Darcan Ş., Gökşen D. Reliability and validity of the diabetes eating problem survey in Turkish children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. JCRPE J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2017;9:323–328. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.4219.
- Coleman, S.E., Caswell, N. Diabetes and eating disorders: an exploration of ‘Diabulimia’. BMC Psychol. 2020;8:101. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-020-00468-4.
- Ferrey A., Ashworth G., Cabling M., Rundblad G., Ismail K. A thematic analysis of YouTube comments on a television documentary titled ‘Diabulimia: The World’s most dangerous eating disorder’. Diabet Med. 2023 May;40(5). doi: 10.1111/dme.15025.
- Gagnon C., Aime A., Belanger C. Psychometric properties of the French Diabetes Eating Problem Survey–Revised (DEPS-R). BAOJ Diabet. 2017;3:1–8.
- Karastogiannidou, C., Giannoulaki, P., Samaras, I., Kotzakioulafi, E., Didangelos, T., Bocsan, I.C., Vassilopoulou, E. The Diabetes Eating Problem Survey-Revised (DEPS-R) in a Greek Adult Population with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Model Comparison Supporting a Single Factor Structure. Nutrients. 2021;13:2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072375.
- Lv W., Zhong Q., Guo J., Luo J., Dixon J., Whittemore R. Instrument context relevance evaluation, translation, and psychometric testing of the diabetes eating problem survey-revised (DEPS-R) among people with type 1 diabetes in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021;18:3450.
- Pinna F., Diana E., Sanna L., Deiana V., Manchia M., Nicotra E., Fiorillo A., Albert U., Nivoli A., Volpe U., et al. Assessment of eating disorders with the diabetes eating problems survey—Revised (DEPS-R) in a representative sample of insulin-treated diabetic patients: A validation study in Italy. BMC Psychiatry. 2017;17:262. doi: 10.1186/s12888-017-1434-8.
- Sancanuto C., Jiménez-Rodríguez D., Tébar F.J., Hernández-Morante J.J. Translation and validation of the Diabetes Eating Problem Survey to screen eating disorders in patients with type-1 diabetes mellitus. Med. Clín. 2017;148:548–554. doi: 10.1016/j.medcle.2016.12.073.
- Saßmann H., Albrecht C., Busse-Widmann P., Hevelke L.K., Kranz J., Markowitz J.T., Marshall L.F., Meurs S., De Soye I.H., Lange K. Psychometric properties of the German version of the Diabetes Eating Problem Survey-Revised: Additional benefit of disease-specific screening in adolescents with Type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2015;32:1641–1647. doi: 10.1111/dme.12788.
- Tarçın, G., Akman, H., Güneş Kaya, D., et al. Diabetes-specific eating disorder and possible associated psychopathologies in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Eat Weight Disord. 2023;28:36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-023-01559-y.
- Torjesen I. Diabulimia: the world’s most dangerous eating disorder. BMJ. 2019 Mar 1;364. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l982.
- Wisting L., Wonderlich J., Skrivarhaug T., Dahl-Jørgensen K., Rø Ø. Psychometric properties and factor structure of the diabetes eating problem survey—Revised (DEPS-R) among adult males and females with type 1 diabetes. J. Eat. Disord. 2019;7:1–7. doi: 10.1186/s40337-018-0232-0.

